Other articles where cerebral hemisphere is discussed: human nervous system: Cerebral hemispheres: Basic organizations of movement, such as reciprocal innervation, are organized at levels of the central nervous system lower than the cerebral hemispheres—at both the spinal and the brainstem level. Examples of brainstem reflexes are turning of the eyes and head toward a light… Learn about the anatomy, function and development of the cerebral hemispheres, the two halves of the brain that are separated by a groove. Find out how the hemispheres are connected, what poles they have, and how they differ in structure and asymmetry. The Cerebral Hemispheres make us human. They include the cerebral cortex (which consists of six lobes on each side: frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insular, and limbic), the underlying cerebral white matter, and a complex of deep gray matter masses, the basal ganglia.From a phylogenetic point of view, the cerebral hemispheres, particularly the cortex, are relatively new.
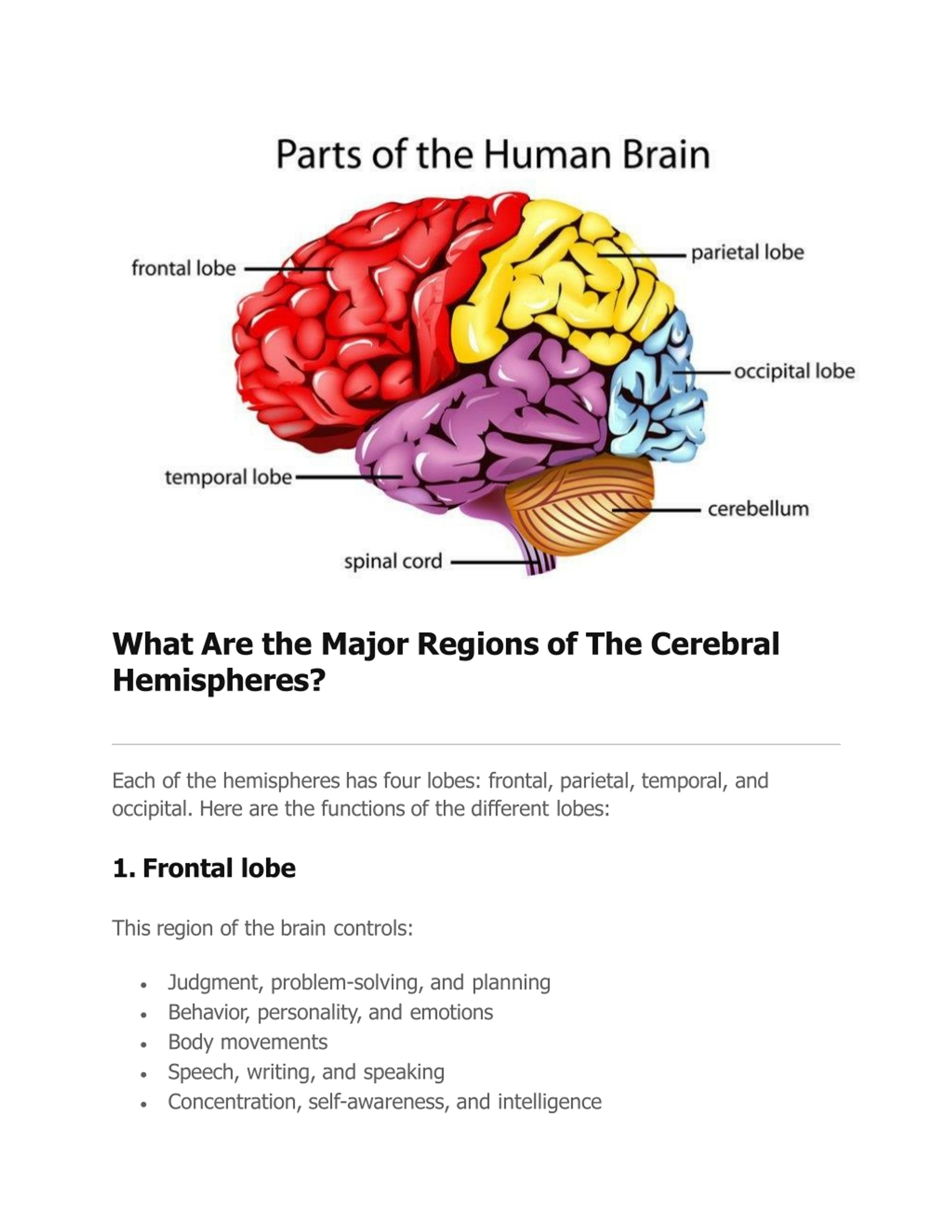
Learn what cerebral hemispheres are, where they are located, and how they control different cognitive functions. Discover the four lobes of each hemisphere and how they can adapt to damage or training.
The cerebral hemispheres consist of an inner core of myelinated nerve fibres, the white matter, and an outer cortex of gray matter.The cerebral cortex is responsible for integrating sensory impulses, directing motor activity, and controlling higher intellectual functions. The human cortex is several centimetres thick and has a surface area of about 2,000 square cm (310 square inches), largely The cerebral hemisphere consists of five lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, and limbic lobe. Each cerebral hemisphere shows superomedial, inferior, and medial surfaces separated by superomedial, inferomedial, and inferolateral borders. The superolateral surface shows the central sulcus that separates the pre-central and post-central gyri. The parietal lobe is divided by the There are two cerebral hemispheres in the brain known as the cerebrum. The cerebral hemispheres are separated by a deep cleft called the longitudinal cerebral fissure, which contains the falx cerebri. However, they are connected below in the middle by white matter commissural fibers called the corpus callosum.Antero-posteriorly, each cerebral hemisphere extends from the frontal to the The cerebral hemispheres are the largest and most prominent part of the brain, consisting of intricate structures responsible for complex cognitive, sensory, and motor activities. Each hemisphere is divided into several lobes, contains various cortical and subcortical structures, and is connected to other parts of the brain by nerve fibers.Cerebral Hemisphere - Anatomy, Location, Diagram, Significance
The cerebral hemispheres consist of an inner core of myelinated nerve fibres, the white matter, and an outer cortex of gray matter.The cerebral cortex is responsible for integrating sensory impulses, directing motor activity, and controlling higher intellectual functions. The human cortex is several centimetres thick and has a surface area of about 2,000 square cm (310 square inches), largely The cerebral hemisphere consists of five lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, and limbic lobe. Each cerebral hemisphere shows superomedial, inferior, and medial surfaces separated by superomedial, inferomedial, and inferolateral borders. The superolateral surface shows the central sulcus that separates the pre-central and post-central gyri. The parietal lobe is divided by the There are two cerebral hemispheres in the brain known as the cerebrum.
The cerebral hemispheres are separated by a deep cleft called the longitudinal cerebral fissure, which contains the falx cerebri. However, they are connected below in the middle by white matter commissural fibers called the corpus callosum.Antero-posteriorly, each cerebral hemisphere extends from the frontal to the The cerebral hemispheres are the largest and most prominent part of the brain, consisting of intricate structures responsible for complex cognitive, sensory, and motor activities. Each hemisphere is divided into several lobes, contains various cortical and subcortical structures, and is connected to other parts of the brain by nerve fibers.
Learn how the cerebral hemispheres are divided into lobes based on their embryological origin, functional roles and topography. See the sulci and gyri that define the boundaries of the frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital and insular lobes.